Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 Vibration and Noise Control Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
3 School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
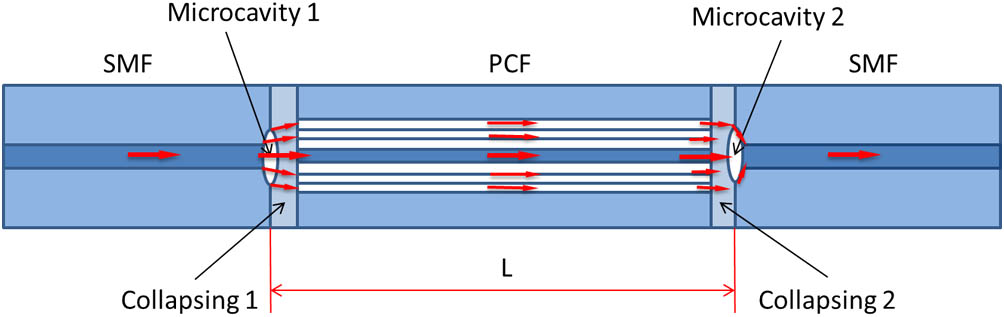
We propose a temperature-insensitive refractive index (RI) fiber sensor based on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. The sensor with high sensitivity and a robust structure is fabricated by splicing a short photonic crystal fiber (PCF) between two single-mode fibers, where two microcavities are formed at both junctions because of the collapse of the PCF air holes. The microcavity with a larger equatorial dimension can excite higher-order cladding modes, so the sensor presents a high RI sensitivity, which can reach 244.16 nm/RIU in the RI range of 1.333–1.3778. Meanwhile it has a low temperature sensitivity of 0.005 nm/°C in the range of 33°C–360°C.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(2): 020603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laser Micro/Nano Fabrication Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
An optical fiber extrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometer (EFPI) is designed and fabricated for refractive index (RI) sensing. To test the RI of liquid, the following two different methods are adopted: the wavelength tracking method and the Fourier-transform white-light interferometry (FTWLI). The sensitivities of sensors with cavity lengths of 288.1 and 358.5 μm are 702.312 nm/RIU and 396.362 μm/RIU, respectively, by the two methods. Our work provides a new kind of RI sensor with the advantages of high sensitivity, mechanical robustness, and low cross sensitivity to temperature. Also, we provide a new method to deal with gold film with a femtosecond laser.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 020602
北京理工大学 机械与车辆学院激光微纳制造研究所, 北京 100081
为了提高光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)温度传感器的测温精度,提出了一种新型的光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)温度传感器的封装方法,并采用二次多项式拟合的方式标定该温度传感器.新的封装方法可以消除FBG温度传感器存在的应力交叉敏感,新的标定方式可以极大地提高光纤温度传感器的测温精度.通过对比光纤温度传感器的线性拟合和二次多项式拟合测温结果,表明这种封装方法结合二次多项式标定使得光纤温度传感器具有很好的稳定性和重复性.在0℃~80℃的温度范围内,曲线拟合度在0.9999以上,测温误差不超过0.13℃,能够满足实际工程应用的需求.
光纤光栅 温度传感器 二次多项式拟合 FBG temperature sensor quadratic polynomial fitting
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A fiber inline interferometric refractive index (RI) sensor consisting of a microchannel and a fiber taper is proposed in this letter. The microchannel is fabricated by combining femtosecond laser micromachining and arc fusion splicing. No subsequent chemical etching process is needed. Three sensors with microchannel widths of 4, 8, and 10 \mu m are prepared. The sensitivity in the RI range from 1.33 to 1.35 is up to ~361.29 nm/RIU at the microchannel width of 8 μm. The sensitivity is ~20 times greater than that of the paired taper-based MZI sensors and long period fiber grating pair MZI sensors.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 220.4610 Optical fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(11): 110603





